Brain Stroke Specialist Doctor in Delhi NCR
Treatment of Brain Stroke in Delhi ?
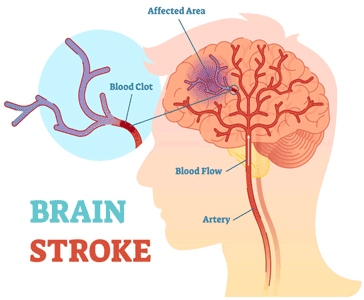
A stroke occurs when the blood circulation in the brain is obstructed or when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and leaks. The blockage or burst prevents blood and oxygen from reaching brain tissue. Without oxygen, the tissues and cells in the brain are damaged and die quickly, resulting in a variety of symptoms.
When brain cells die, they do not regenerate and can cause devastating damage, sometimes resulting in physical, cognitive, and mental disabilities. It is critical that proper blood flow and oxygen flow to the brain be restored as soon as possible.
Brain Stroke Types:-
There are two types of brain stroke.
1. Hemorrhagic Stroke accounts for 20% of all brain strokes.
. A blood clot forms inside a diseased or damaged artery in the brain as a result of atherosclerosis (cholesterol-containing plaque), obstructing blood flow.
. A clot or small piece of plaque formed in one of the arteries leading to the brain or in the heart is pushed through the bloodstream and lodges in narrower brain arteries, resulting in an embolic stroke. Because of the clogged vessel, the blood supply to the brain is cut off. Intracerebral or subarachnoid hemorrhage can cause hemorrhagic stroke.
2. Intracerebral Hemorrhage is bleeding within the brain tissue; the most common cause is changes in the arteries caused by long-term hypertension.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is defined as bleeding between the surface of the brain and the skull. The most common causes are cerebral aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations (AVM).
Looking for a dedicated brain stroke specialist to guide you through the treatment of brain stroke? Dr. Hrishikesh Chakrabartty is here to help. With extensive experience in the treatment of brain stroke, Dr. Chakrabartty can provide the expert care and support you need. Our team is dedicated to providing the highest quality treatment options and personalized care plans to help you on your road to recovery. Contact us today to learn more and schedule a consultation with our doctor of brain stroke.
What are the signs of a stroke in the brain?
The range and severity of early stroke symptoms vary greatly, but they all share the symptom of sudden onset. The following are common signs and symptoms of a brain stroke:
- Numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg that occurs unexpectedly, particularly on one side of the body.
- Unexpected perplexity
- Speaking difficulties
- Speech comprehension difficulty
- Sudden vision loss in one or both eyes
- Dizziness and sudden difficulty walking
- Lack of coordination or loss of balance
- Severe headache with vomiting or unconsciousness that occurs suddenly
Its Very important to recognize the sign and symptom of Stroke on time to get the Best Treatment for Stroke so as to avoid the major loss in Brain.
What are the risk factors for a stroke?
Although strokes are more common in the elderly, they can happen to anyone at any age. Understanding the risk factors for stroke and recognising the symptoms may help prevent a stroke. Early detection and treatment increases the likelihood of complete recovery.
Modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors are the two types of risk factors.
Modifiable risk factors include:
Modifiable risk factors are risk factors that are controllable and treatable, such as:
- Tobacco use raises the risk of stroke. When oral contraceptives are used in conjunction with smoking, the risk of stroke increases. Long-term secondhand smoke exposure may increase the risk of stroke, according to new research.
- High blood pressure: The most important risk factor for stroke is blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg.
- Carotid artery disease or other artery disease: The carotid arteries in the neck transport blood to the brain. A blood clot blocks a carotid artery that has been narrowed by fatty deposits caused by atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes: Diabetes, especially when left untreated, increases the risk of stroke and has numerous other serious health consequences.
- High levels of total cholesterol (240 mg/dL or higher), LDL (bad)Lower-than-40 mg/dl cholesterol may increase the risk of stroke.
- Obesity and physical inactivity: Being inactive, obese, or both can increase your risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
- Cardiac diseases such as AF (atrial fibrillation) and others, as well as large and small vessel disease, all increase the risk of having an ischemic stroke.
If you are having any of the sign and symptoms and are into any of the above Risk Factor. You can connect with Best Neurosurgeon in Delhi for the expert advice.
Risk factors that are not modifiable or controllable include:
- Strokes have an impact on people of all ages, including children. However, the risk increases with age.
- Strokes are more common in men than in women. Women, on the other hand, account for more than half of all stroke deaths. Postmenopausal women are just as vulnerable as men.
- Stroke risk is increased by family history and certain genetic disorders.
- Previous stroke increases the likelihood of recurrent stroke.
PREVENTION
How can I lower my risk of having a stroke or completely avoid one?
There are numerous things you can do to lower your chances of having a stroke. While this does not mean you can avoid having a stroke, it does reduce your chances. You can take the following actions:
- Improve your way of life. Eating a healthy diet and incorporating exercise into your daily routine can help improve your health. You should also ensure that you get enough sleep (the recommended amount is seven to eight hours).
- Avoid risky lifestyle choices or make behavioral changes. Smoking and tobacco use, including vaping, recreational drug use or prescription drug abuse, and alcohol abuse are all risk factors for stroke. It is critical to either stop or never start these. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is critical that you consult with your healthcare provider. Your provider can provide you with advice and resources to help you change your lifestyle in order to avoid these behaviors.
- Take control of your health conditions and risk factors. Obesity, abnormal heart rhythms, sleep apnea, high blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes, or high cholesterol are all conditions that can increase your risk of having an ischemic stroke. If you have one or more of these conditions, it is critical that you do everything possible to manage them, particularly by taking medications, such as blood thinners, as prescribed by your provider. By doing so earlier in life, you can avoid serious stroke-related problems later in life.
- Annually, visit your primary care provider for a checkup or wellness visit. Yearly wellness visits can detect health problems, particularly those that contribute to strokes, long before you notice any symptoms.
How are strokes identified?
A stroke can be diagnosed by a healthcare provider using a neurological examination, diagnostic imaging, and other tests. During a neurological examination, you will be asked to perform tasks or answer questions. The provider will look for telltale signs of a problem with how part of your brain works as you complete these tasks or answer these questions.
When a healthcare provider suspects a stroke, the following tests are performed:
- CT scan stands for computed tomography.
- Blood tests in a laboratory (looking for signs of infections or heart damage, checking clotting ability and blood sugar levels, testing how well kidneys and liver function, etc.).
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) to ensure that a heart problem isn’t the source of the problem.
- Scanners for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Though less common, an electroencephalogram (EEG) can rule out seizures or other problems.
Best Hospital for Brain Stroke Doctors in Delhi NCR
Treatment
The emergency treatment for a stroke depends on whether it is an ischemic stroke or a stroke with bleeding into the brain (hemorrhagic).
Stroke caused by ischemia (Ischemic Stroke)
Doctors must restore blood flow to the brain as soon as possible to treat an ischemic stroke.. This may be done with:
Emergency IV Medication to treat an ischemic stroke, doctors must restore blood flow to the brain as soon as possible reaches to emergency. If administered intravenously, clot-busting drugs must be administered within 4.5 hours of the onset of symptoms. The earlier these medications are given, the better results are . Quick treatment not only improves your chances of survival but also may reduce complications.
An IV injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (TPA), also known as alteplase (Activase) or tenecteplase, is the gold standard treatment for ischemic stroke (TNKase). A TPA injection is usually given through a vein in the arm within the first three-four hours. TPA can be given up to 4.5 hours after stroke symptoms appear..
This medication improves blood flow by dissolving the blood clot that caused the stroke. It may help people recover more fully from a stroke if the cause of the stroke is removed as soon as possible.
Emergency endovascular procedures. Ischemic strokes are sometimes treated directly inside the blocked blood vessel by doctors. Following an ischemic stroke, endovascular therapy has been shown to improve outcomes and reduce long-term disability. These steps should be taken as soon as possible:
Medications that are administered directly to the brain. Doctors thread a long, thin tube (catheter) through an artery in the groyne and into the brain to deliver TPA directly to the site of the stroke. This treatment has a slightly longer time window than injected TPA, but it is still limited.
Other methods
Your doctor may recommend a procedure to open up a plaque-clogged artery to reduce your risk of having another stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Carotid endarterectomy. Carotid arteries are blood vessels that run along each side of the neck, supplying blood to the brain. This procedure removes plaque from a carotid artery, potentially lowering the risk of an ischemic stroke. A carotid endarterectomy is not without risk, particularly for people who have heart disease or other medical conditions.
Stents and angioplasty. During an angioplasty, a surgeon inserts a catheter into the carotid arteries via a groin artery. After that, a balloon is inflated to widen the narrowed artery. The opened artery can then be supported by a stent.
Stroke with haemorrhage
Controlling the bleeding and reducing the pressure in the brain caused by the excess fluid are the primary goals of emergency treatment for hemorrhagic stroke
Surgery. If the area of bleeding is large, your doctor may perform surgery to remove the blood and relieve pressure on the brain. Blood vessel damage caused by hemorrhagic strokes can also be repaired surgically.. After a stroke or if an aneurysm, arteriovenous malformation (AVM), or other type of blood vessel problem caused the hemorrhagic stroke, your doctor may recommend one of these procedures.
Clipping during surgery. To stop blood flow to the aneurysm, a tiny clamp is placed at its base. This clamp can prevent an aneurysm from bursting or prevent a recently hemorrhaged aneurysm from bleeding again
Coiling (endovascular embolization). The surgeon will place tiny detachable coils into the aneurysm using a catheter inserted into a groin artery and guided to the brain. This prevents blood from flowing into the aneurysm and causes it to clot.
AVM removal via surgery. If the AVM is in an accessible area of the brain, surgeons may be able to remove it. This eliminates the possibility of rupture and reduces the possibility of hemorrhagic stroke. However, removing an AVM is not always possible if it is located deep within the brain, is large, or would have a negative impact on brain function.
Radiosurgery with stereotactic accuracy. Stereotactic radiosurgery is an advanced minimally invasive treatment that uses multiple beams of highly focused radiation to repair blood vessel malformations.