Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical treatment used to treat symptoms of neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. It involves the implantation of electrodes in specific areas of the brain to help regulate abnormal electrical impulses that cause these disorders.
Causes:
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder are caused by abnormal electrical activity in certain areas of the brain. This can occur due to a variety of reasons, including genetic mutations, environmental factors, and age-related changes in the brain. While the exact cause of these disorders is not known, DBS is used to help alleviate the symptoms associated with these conditions.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of neurological disorders vary depending on the specific condition. For example, in Parkinson’s disease, symptoms may include tremors, rigidity, and difficulty with movement. Essential tremor may cause shaking in the hands, head, or voice, while dystonia may cause muscle spasms and abnormal postures. Obsessive-compulsive disorder may cause repetitive behaviors or obsessive thoughts. DBS is used to treat these symptoms and improve quality of life for patients.
Treatment
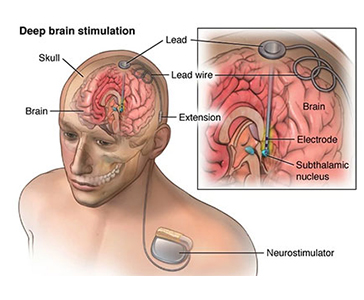
DBS involves the implantation of electrodes in specific areas of the brain that are associated with the symptoms of the neurological disorder being treated. These electrodes are connected to a pulse generator that is implanted under the skin, usually in the chest or abdomen. The generator sends electrical impulses to the brain to help regulate abnormal activity and improve symptoms.
Before the surgery, the patient undergoes a series of tests to determine the best location for the electrodes. The surgery itself typically involves drilling small holes in the skull to place the electrodes, which are then connected to the pulse generator. The patient may need to stay in the hospital for a few days after the surgery for monitoring.
Following the surgery, the pulse generator is programmed to deliver electrical impulses to the brain. The patient will need to make regular visits to the doctor for adjustments to the programming, which can help improve symptoms further. DBS is not a cure for neurological disorders, but it can significantly improve quality of life for those living with these conditions.
How successful is Deep Brain Stimulation ?
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has been used as a treatment for neurological disorders for several decades. The procedure involves implanting electrodes in specific areas of the brain to help regulate abnormal electrical impulses that cause symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and difficulty with movement. While DBS is not a cure for these conditions, it has been shown to be a highly successful treatment option for many patients.
DBS can significantly improve symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. For example, in patients with Parkinson’s disease, DBS has been shown to reduce tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement) by up to 80%. In patients with essential tremor, DBS has been shown to reduce tremors by up to 90%. In patients with dystonia, DBS has been shown to improve muscle spasms and abnormal postures by up to 60%.
The success of DBS depends on several factors, including the specific condition being treated, the location of the electrodes, and the patient’s overall health. However, overall, DBS has a high success rate in improving symptoms and quality of life for patients with neurological disorders.
It is important to note that DBS is not without risks. Like any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection, bleeding, and other complications. In addition, some patients may experience side effects from the electrical stimulation, such as speech difficulties, cognitive changes, or sensory disturbances. However, these risks are generally low and can be managed through careful patient selection, monitoring, and programming of the DBS device.
Overall, DBS is a highly successful treatment option for many patients with neurological disorders. While it is not a cure, it can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life, allowing patients to better manage their conditions and enjoy a better quality of life.